Have you ever paused to ask: the inventory and stock difference? At first glance, the two terms seem interchangeable, twin threads in the fabric of supply and demand. But beneath the surface, a quiet yet critical distinction exists. And recognizing it? That might just be the edge your business needs to thrive.
Understanding the inventory and stock difference isn’t just a matter of semantics, it’s about clarity, control, and strategic foresight. It’s the kind of knowledge that empowers accountants to track assets more precisely, helps financial managers improve cash flow, and enables business owners to make sharper, smarter decisions. Inventory and Stock Difference
In this article, we’ll journey beyond the basics to explore how businesses can fine-tune their inventory strategy for maximum efficiency. We’ll ask the hard questions:
- Are you valuing your inventory correctly?
- Is your stock turnover ratio formula revealing hidden insights, or masking them?
- Could your business benefit from a modern barcode system for inventory management?
From inventory valuation techniques and reorder level of inventory strategies to practical tools like the inventory aging report in Excel, we’ll dive deep into the methods that turn numbers into decisions.
Read more: Importance of ABC Analysis in UAE
The Key Inventory and Stock Difference Explained
At first glance, inventory and stock differences might appear interchangeable, but a deeper dive reveals nuanced distinctions that impact accounting and operational strategies.
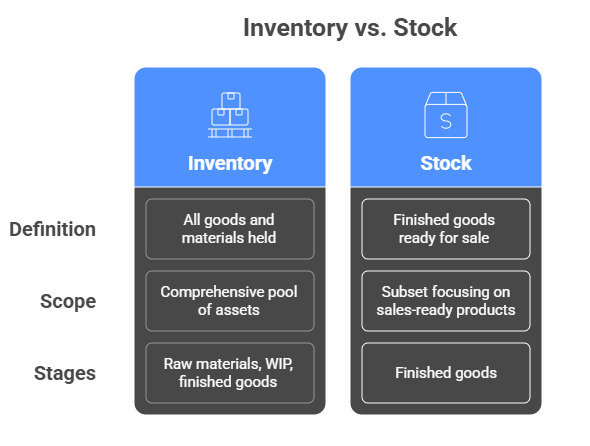
ِA- Inventory:
Encompasses all goods and materials held by a business, from raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), to finished goods awaiting sale. It represents a comprehensive pool of assets crucial to production and sales cycles.
B- Stock:
More narrowly, it typically refers to finished goods ready for sale to customers. It’s a subset of inventory focusing solely on retail or sales-ready products.
| Aspect | Inventory | Stock |
| Scope | Raw materials, WIP, finished goods | Finished goods ready for sale |
| Purpose | Support production & operations | Fulfill customer demand |
| Accounting Treatment | Broad asset category | Subset of inventory in financials |
| Management Focus | Comprehensive tracking & valuation | Sales & replenishment optimization |
Understanding this difference underpins key operational decisions and financial health indicators like the stock turnover ratio formula, which measures how fast stock sells over a period.
Read more: Fixed Asset Register
💡 Streamline Your Inventory with mazeed!
Use mazeed accounting software to track stock in real-time, reduce errors, and keep your business running smoothly.
Why Does This Distinction Matter?
1- Accounting and Valuation
- Inventory is categorized as a current asset on the balance sheet, but different components (raw materials, WIP, finished goods) may be valued differently using techniques like FIFO, LIFO, or Weighted Average Cost.
- Stock, as the sellable portion, directly affects revenue and cost of goods sold (COGS), influencing profitability calculations.
2- Operational Strategy
- Stock levels determine reorder points and influence customer satisfaction.
- Inventory, in a broader sense, informs supply chain decisions, production scheduling, and procurement strategies.
3- Inventory Control Applications
- Managing inventory requires systems that track not only what is available to sell (stock), but also what is in production, awaiting assembly, or inbound from suppliers.
The Strategic Application of Inventory Control
Inventory control isn’t just about keeping track; it’s about mastering a dynamic system that balances supply and demand, reduces costs, and optimizes cash flow.
1. The Role of Inventory Control Applications
The application of inventory control integrates methodologies and technologies designed to monitor inventory levels, forecast demand, and automate reordering processes.
- Effective inventory control helps establish the reorder level of inventory, the threshold triggering new purchases to avoid stockouts.
- It mitigates risks of overstocking or obsolete inventory, a major challenge tackled using tools like the inventory aging report in Excel, which highlights items lingering beyond their optimal turnover time.
2. Barcode System for Inventory Management
Modern inventory control relies heavily on automation. A barcode system for inventory management enables rapid, accurate data capture, minimizing human error and speeding up processes.
- Barcodes facilitate real-time tracking of both inventory and stock difference, ensuring transparency across procurement, warehousing, and sales.
- Integration with inventory software Dubai solutions makes barcode systems indispensable for businesses aiming for scalable, error-proof inventory practices.
Read more: Accounting Standards in UAE
Inventory Valuation Techniques
One of the most underestimated tools in achieving operational agility and financial precision is inventory analysis. This practice goes far beyond counting items on shelves; it is a data-driven discipline that empowers businesses to make informed decisions, reduce waste, maximize cash flow, and improve customer satisfaction.
What is Inventory Analysis?
Inventory analysis refers to the process of examining inventory data to identify patterns, track trends, and uncover inefficiencies. It evaluates what products are in stock, how quickly they’re selling, what needs to be reordered, and what may soon become obsolete. When done properly, inventory analysis offers real-time visibility into business health and exposes areas of risk and opportunity.
Why Inventory Analysis Matters
Common Inventory Valuation Techniques Used by Businesses
A- FIFO (First In, First Out)
- Assuming the earliest purchased goods are sold first.
- Reflects current market costs more accurately in periods of inflation.
B- LIFO (Last In, First Out)
- Assuming the most recently acquired goods are sold first.
- Can lower taxable income during inflation but is not accepted under IFRS.
C- Weighted Average Cost
- Averages the cost of all inventory items available for sale.
- Smooths out price fluctuations over time.
D- Specific Identification
- Tracks the exact cost of each item sold.
- Ideal for unique or high-value products.
Each method affects how inventory and stock differences appear on the balance sheet and impacts key ratios like the stock turnover ratio formula, providing insights into how effectively stock is managed and sold.
Inventory Analysis

Conducting a thorough inventory analysis helps businesses:
One practical tool is the inventory aging report in Excel, which categorizes stock by age and movement frequency. This report can be generated and customized easily in Excel, making it accessible for small and medium enterprises that may not have advanced software yet.
Read more: What is Contra Entry?
The Vital Practice of Stock Take
No inventory management strategy is complete without periodic physical verification, commonly known as a stock take.
- Regular stock takes help reconcile physical stock with system records.
- They identify shrinkage, theft, or errors in recording.
- Stock taking accuracy feeds back into the application of inventory control systems to maintain reliable data integrity.
Businesses often use barcode scanning tools during stock takes to accelerate the process and reduce errors, integrating this data seamlessly into inventory software Dubai platforms.
Stock Turnover Ratio Formula
A few notes ring louder than the stock turnover ratio formula. It is a financial and operational melody that reveals how swiftly a company is converting its inventory into revenue. A high turnover can signify lean operations and high demand; a low one might whisper inefficiencies, overstocking, or waning interest in your products.
This KPI is not just a number. It’s a story, of how you buy, how you sell, and how well your inventory strategy aligns with your business pulse.
What Is the Stock Turnover Ratio?
The stock turnover ratio, also known as the inventory turnover ratio, measures how many times a company’s inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. It gauges the efficiency with which inventory is managed and indicates how well a business is performing in terms of product movement.
Stock Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Stock
- A high turnover ratio indicates efficient sales and inventory and stock difference management.
- A low ratio may signal overstocking, obsolescence, or weak sales.
Tracking this ratio over time allows firms to adjust purchasing and production strategies, thus optimizing the reorder level of inventory and stock difference and preventing excess holding costs.
💡 Software & Exports Together
Get powerful inventory tools with certified financial and operational experts to optimize stock, reduce costs, and prevent losses.
Why Businesses in Dubai Should Invest in Inventory Software Dubai
Dubai’s competitive market demands agility and precision. The inventory software Dubai market offers tailored solutions integrating barcode systems, automated reorder alerts, inventory aging analysis, and real-time stock management.
Read more: Accrual Accounting Journal Entries
Key Benefits of Inventory Software in Dubai’s Business Landscape
- Real-Time Visibility and Control
- Localization and Tax Compliance
- Integration with Barcode Systems
- Advanced Inventory Valuation Techniques
- Optimized Reorder Management
Comparing Key Inventory Control Tools and Their Benefits
| Tool | Purpose | Key Benefits |
| Barcode System | Automated inventory data capture | Accuracy, speed, reduced errors |
| Inventory Aging Report in Excel | Analyze inventory age and turnover | Identifies slow-moving stock |
| Inventory Software Dubai | Comprehensive inventory management | Real-time tracking, automation |
| Stock Take | Physical inventory verification | Ensures data integrity and accuracy |
| Inventory Valuation Techniques | Financial assessment of inventory | Accurate reporting, tax compliance |
Is stock an example of inventory?
Yes. Stock is a subset of inventory. Inventory includes all items a business owns for sale, production, or operations (raw materials, work-in-progress, finished goods, supplies). Stock usually refers only to the finished goods ready to be sold.
What is the difference between physical stock and inventory?
– Physical stock: The actual goods available and counted in the warehouse or store.
– Inventory: A broader term that covers physical stock plus raw materials, work-in-progress, spare parts, and sometimes consumables.
Is inventory the same as stock taking?
No.
– Inventory is the collection of goods owned.
– Stock taking (or stock count) is the process of physically counting and verifying the items in invento
What is the difference between inventory asset and stock?
– Inventory asset: The total value of goods a company owns (recorded as a current asset on the balance sheet).
– Stock: The specific items intended for sale to customers. Inventory asset is about value; stock is about quantity and type.
Are inventory and stock the same?
Not exactly. In everyday business language, they are sometimes used interchangeably. However:
– Inventory is the broader accounting term.
– Stock refers specifically to products meant for sale.
What is a stock?
Stock is the collection of goods or products a business keeps on hand to sell to customers, such as clothes in a retail shop or medicine in a pharmacy.
What is stock and its example?
Stock means goods held for resale.
Example: A bookstore’s stock includes novels, textbooks, and magazines available on its shelves.
What is a stock short answer?
Stock is the finished goods a business sells to customers.
How many types of stocks are there?
There are several classifications, depending on context:
– In accounting/operations: Raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
– In investment/finance: Common stock and preferred stock.
What are the three main types of stock?
– Raw materials – items used in production.
– Work-in-progress (WIP) – semi-finished goods.
– Finished goods – ready-to-sell products.
What are 5 good stocks?
In the business/inventory sense, “good stocks” means essential categories, e.g.:
1- Raw materials
2- Work-in-progress
3- Finished goods
4- Maintenance, repair & operations (MRO) items
5- Safety stock (buffer for demand fluctuations)
What are the four basic stocks?
The four common categories are:
1- Raw materials
2- Work-in-progress (WIP)
3- Finished goods
4- MRO goods (Maintenance, Repair, Operations)
Disclaimer: This publication is for informational purposes only and should not be considered professional or legal advice. While we strive for accuracy, we make no guarantees regarding completeness or applicability. mazeed, its members, employees, and agents do not accept or assume any liability, responsibility, or duty of care for any actions taken or decisions made based on this content. For official guidance, please refer to the UAE Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Authority.




